You can shed fat easily and lose weight by practicing this type of intermittent fasting in addition to the benefit of regulating your hormones. It allows you to eat normally for a greater period of time and short periods for eating less. This pattern may be more conducive for many people.
The 5:2 intermittent fasting simply means eating normally for 5 days of the week and eating less in the remaining 2 days. On the two fasting days, men should consume only 600 calories while women should do 500 calories.
Who should and should not try intermittent fasting?
IF is generally safe for most healthy people. However, ill people would need to consult with their general practitioner before they embark on the program.
You are not a good candidate for IF if you are:
- Pregnant or nursing a child (note that IF can help restore your body when you are done with nursing your child)
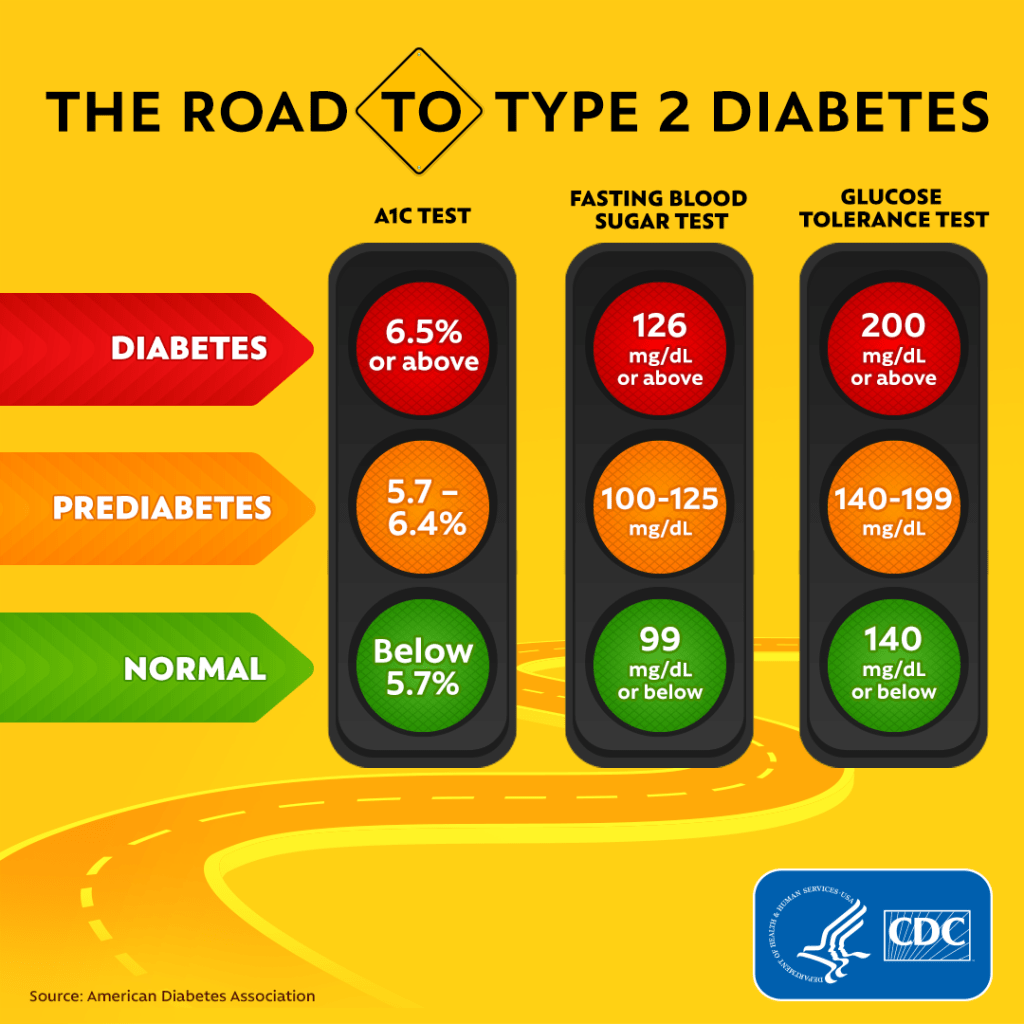
- Diabetic. You must be under medical supervision
- Have eating disorders or at risk of developing one
- a child or under 18, it must be done under strict supervision to avoid nutritional issues
You are a good candidate for IF if you are:
- You currently eat unhealthily
- Addicted to sugary foods or empty calories
- Need a simple meal plan
What you can and cannot eat on the 5:2 fast diet:
Allowed foods:
- Fresh vegetables
- Fresh fruits
- Lean meat (eg. mutton, pork) and poultry
- Fish and seafood
- Low-fat dairy
- Whole grains
- Legumes (such as beans)
- Nuts and seeds
- Healthy fats (such as avocados, olive oil, coconut oil, flaxseed oil)
- Limited sugary foods like honey
What to avoid:
- Fast foods
- Deep fried foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Sugary treats
- Soda
On fasting days, eating less is what makes the program viable. And also, you should also take the opportunity to eat nutrient rich foods. And it doesn’t mean you shouldn’t eat 3 square meals. It’s just the amount of calories that matter. For example, egg toast with tomatoes is not calorie-packed but nutritious. It’s all about eating less.
IF has so many variations that it allows you to fit in and enjoy the benefits that come with it. It is important that we fast in order to optimize our health.